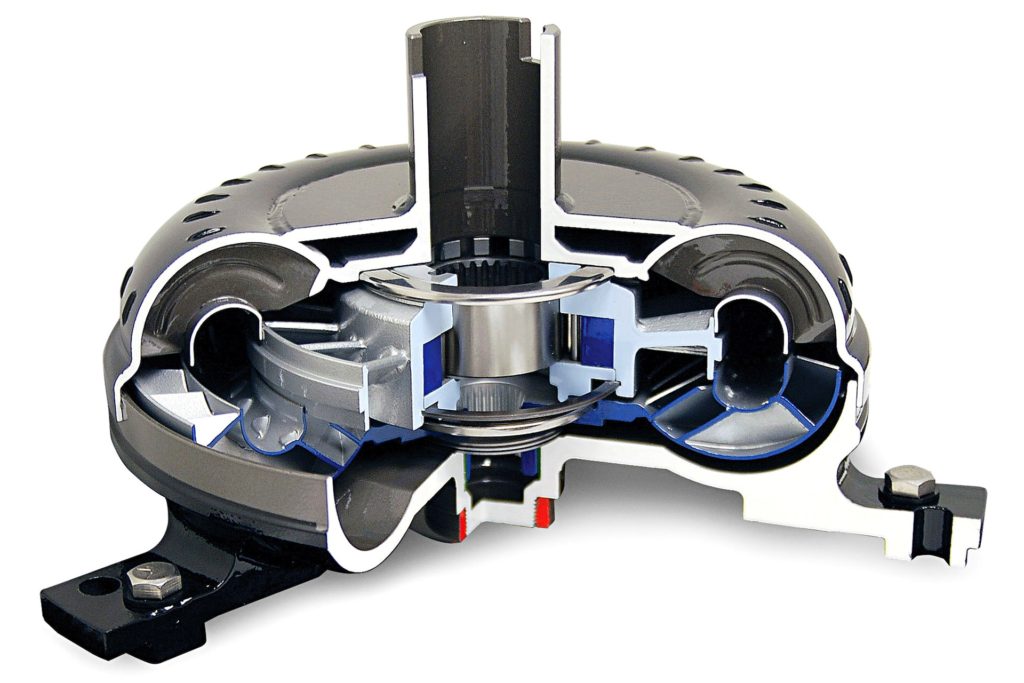
Torque Converter Basics And How To Choose
A torque converter is a device that transfers power from the engine to the transmission in an automatic transmission vehicle. It does this by using the principle of fluid coupling, which means that the torque converter can multiply the engine’s torque output.
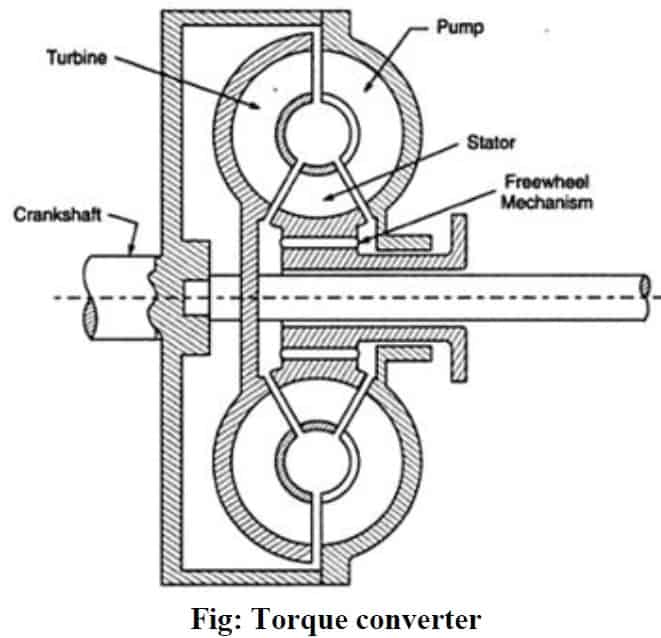
Torque Converter Parts: Impeller, Turbine, Stator
The torque converter is made up of three main parts: the impeller, the turbine, and the stator. The impeller is connected to the engine and spins at the same speed as the engine. The turbine is connected to the transmission and spins at the speed of the transmission. The stator is located between the impeller and the turbine and helps to direct the flow of fluid.
When the engine is running, the impeller spins and creates a vortex of fluid. This vortex of fluid then flows to the turbine, which spins the turbine and the transmission. The amount of torque that is transferred from the engine to the transmission depends on the speed of the impeller and the turbine.
The torque converter can multiply the engine’s torque output by up to 2.5 times. This means that if the engine is producing 100 lb-ft of torque, the torque converter can multiply that by 250 lb-ft of torque. This multiplication of torque is what allows automatic transmission vehicles to get off the line quickly and smoothly.
The torque converter is a vital component of the automatic transmission system. It allows the transmission to smoothly and efficiently transfer power from the engine to the wheels. Without a torque converter, automatic transmission vehicles would not be able to function properly.
Types Of Torque Converters: Single, Dual, and Lock-Up
There are three main types of torque converters: single-stage, dual-stage, and lockup. Single-stage torque converters are the most common type. They are used in most automatic transmission vehicles. Dual-stage torque converters are designed for high-performance vehicles. They have two stages of torque multiplication, which allows them to provide even more torque to the transmission. Lockup torque converters lock up the converter, which transfers 100% of the engine power to the transmission. This is beneficial for fuel economy, as it eliminates the slippage that occurs in a non-lockup torque converter.
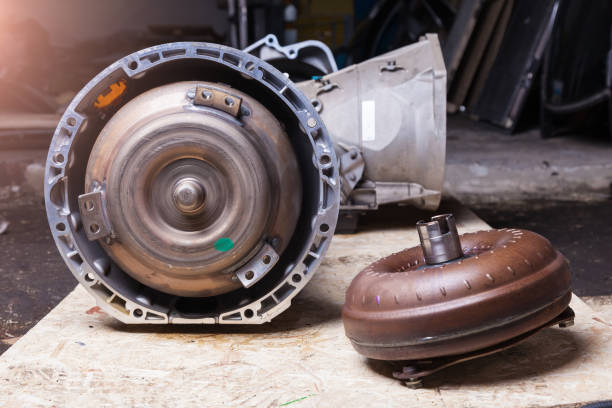

Torque Converter Stall Speed
The best stall speed for your car will depend on your driving habits and needs. If you are looking for a car that is fuel-efficient, you will want a torque converter with a low stall speed. If you are looking for a car that has good performance, you will want a torque converter with a high stall speed.
- Low stall speed: A low stall speed means that the torque converter will start transferring power at a lower RPM. This is good for fuel economy, as it means that the engine doesn’t have to work as hard to get the car moving. However, a low stall speed also means that the car won’t have as much low-end torque, which can make it difficult to get off the line quickly.
- High stall speed: A high stall speed means that the torque converter will start transferring power at a higher RPM. This is good for performance, as it means that the car will have more low-end torque. However, a high stall speed also means that the car will use more fuel, as the engine will have to work harder to get the car moving.
Engine size: A larger engine will have a higher stall speed than a smaller engine. This is because a larger engine has more torque, which means that it can start transferring power at a higher RPM.
Choosing The Right Torque Converter
When choosing a torque converter, you need to consider the horsepower and torque output of your engine, as well as the type of transmission you have. You also need to consider the stall speed.
Generally speaking, if you have a car with a big cam and it makes lots of horsepower, you’ll need a higher stall speed as well. Not only will this give you the best performance, but if your idle is higher then you need a higher stall so it’s not trying to go forward when you’re at a stop light.
Stall speed is the RPM at which the converter stops transferring power. A higher stall speed will give you more low-end torque, but it will also reduce fuel economy.
- Check the manufacturer’s recommendations for your vehicle.
- Buy a quality torque converter from a reputable manufacturer.
- Have the torque converter installed by a qualified mechanic.
Quick Notes:
- The torque converter is a fluid coupling, which means that it uses the force of moving fluid to transfer power.
- The impeller is the part of the torque converter that is connected to the engine. It spins at the same speed as the engine.
- The turbine is the part of the torque converter that is connected to the transmission. It spins at the speed of the transmission.
- The stator is located between the impeller and the turbine. It helps to direct the flow of fluid and improve the efficiency of the torque converter.
- The stall speed is the RPM at which the torque converter stops transferring power. A higher stall speed will give you more low-end torque, but it will also reduce fuel economy.
As you can see, there’s a lot of science and many variables for a torque converter. We have a full selection of different torque converters available here at SS396.com. Unfortunately, an article like this won’t be able to accurately pick the right converter for your car, so give our friendly techs a call at (203) 235-1200 and they will be happy to help!